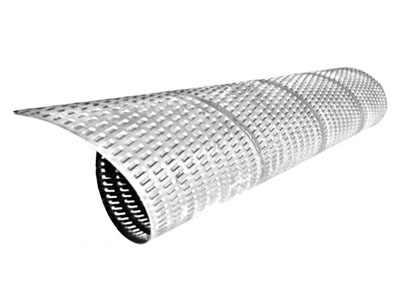
Pressure-fed Sieve Bend Screen Design Calculation: The Key to Efficient Solid-Liquid Separation
In modern industry and urban sewage treatment, pressure-fed sieve bends are becoming a preferred choice for separating solids from liquids. They are efficient and save energy, making them ideal for treating wastewater before further processing.
Now we explain the design and calculation principles of pressure-fed sieve bends and their significant advantages in practical applications

1. Design and calculation principles of pressure-fed sieve bends
The design and calculation of pressure-fed sieve bends are based on water flow dynamics and solid-liquid retention mechanisms. Its goal is to maximize the solid separation efficiency while ensuring the circulation efficiency.
The following are the key design steps:
1.1 Determination of slot width
The slot width is the core parameter that affects the filtration accuracy and should be reasonably selected based on the particle size of suspended particles in the wastewater:
For wastewater from printing and dyeing, papermaking and other industries, it is recommended that the screen slot width is usually less than 2000μm;
If finer particles (such as pharmaceutical wastewater) need to be treated, a smaller slot width can be used.
1.2 Calculating Water Flow Area
The water flow area is directly related to the processing capacity per unit time .
The water flow area is an important parameter affecting the filtration efficiency of the sieve bend. When designing, it is necessary to ensure that the filtration capacity of the screen meets the processing requirements based on the wastewater flow rate and the screen slot width.
1.3 Head loss control
Head loss is an inevitable energy loss in the screen filtration process. When designing, it is necessary to optimize the screen slot width and structure to reduce head loss and improve filtration efficiency.
2. Main Advantages of pressure-fed sieve bends
2.1 High-Efficiency Separation
The stainless steel sieve bend screens can remove solids, fibers, and particles from wastewater very effectively. This helps reduce the load on later treatment steps and extends equipment life.
2.2 Energy-Saving and Eco-Friendly
Pressure-fed sieve bends don’t need electricity or motors. They use the natural flow and gravity of water to separate solids, making them low-cost to run.
2.3 Easy to Maintain
The sieve bends are simple in design, often with self-cleaning features. They don’t get blocked easily and are low maintenance, making them great for long-term use.
3. Common Applications of pressure-fed sieve bends
3.1 Industrial wastewater pretreatment
In industries like dyeing, paper-making, or food processing, pressure-fed sieve bends remove solids like fibers, sludge, and grease. This improves water reuse and reduces pollution.
3.2 Urban sewage treatment
Pressure-fed sieve bends are used in municipal drainage systems and sewage plant pretreatment units. They help catch big particles, keeping the next treatment steps running smoothly.
3.3 Fine Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals
For processes needing very clean separation, pressure-fed sieve bends help remove solid materials early, reducing pressure on more advanced filtering equipment like membranes or centrifuges.